Point-of-care integrated sample-sparing system for monitoring sepsis
A microfluidic system
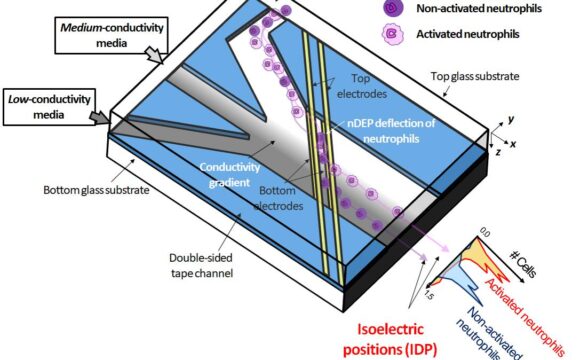
Sepsis is a systemic inflammation that arises for serious bloodstream infection. In the United States, more than 1 million people are hospitalized annually for sepsis. It is a fast-moving disease, and there is currently no method of rapidly monitoring patients’ sepsis state and responses to treatment. This team has developed and tested an integrated microfluidic system for the label-free isolation and downstream functional assessment of leukocytes from less than 50 microliters of peripheral blood in a few minutes. The method uses a microfluidic device that assesses leukocyte activation by measuring the electrical properties of the cells. The measurements from this approach were more highly correlated to sepsis severity than the current clinical practice of measuring peripheral blood leukocyte counts and differentials, and the method supplements vital signs monitoring by assessing the immune cell response. This project aims to commercialize a sepsis monitoring system based on this technology.

Microfluidics device helps diagnose sepsis in minutes
When time matters in hospitals, automated system can detect an early biomarker for the potentially life-threatening condition.